Less Trust, More Truth: Mastering Web 3.0
Karolina Kondrak
9 min of reading
In 1991, the first website emerged, marking the dawn of the internet age. Back then, some people thought it would be just a passing fad—a digital experiment that might fade away. Little did they know that it was the beginning of a transformation that would shape the future of human interaction and information exchange.
 Source: The excerpt is comes from the Daily Mail, December 5, 2000 and was found on Twitter.
Source: The excerpt is comes from the Daily Mail, December 5, 2000 and was found on Twitter.
Today, over 5 billion people globally are regular internet users, a testament to the profound impact the World Wide Web has had on our lives. Yet, amidst the familiarity of social media, e-commerce, and streaming services, whispers of change persist. Web 3.0 is on the horizon, and it has the potential to be as groundbreaking as Web 1.0 was in the '90s. While some might still not fully grasp what Web3 is or wonder if it's just a passing trend, we're eagerly embracing what lies ahead. The shift to Web 3.0 represents more than just an upgrade; it's a fundamental reimagining of the internet—a move towards a decentralized, user-centric, and transparent digital era.
Web Evolution: From Static to Decentralized
From the static pages of Web 1.0 to the dynamic user-generated content of Web 2.0, the internet has transformed our world. Now Web 3.0 has entered the fray. Let's compare three web eras.
Web 1.0: The Static Web
In the early days, the internet was static, with read-only webpages and limited interactivity. Information retrieval was a challenge, and content creation was confined to a select few. It was the beginning of the digital age but lacked the dynamic nature we've come to know today.
Web 2.0: The Dynamic Web
Web 2.0 brought about a seismic shift, empowering users to actively engage with web content. Social media, user-generated platforms, and the rise of smartphones transformed the internet into a dynamic, collaborative space. The internet became a place where people not only consumed information but actively contributed to it. People could create, share, and engage instantly.
The development of Web 2.0 was made possible by technologies such as Javascript, HTML5, and CSS3. These paved the way for the creation of major services (e.g., Facebook, Google, YouTube) and e-commerce platforms like Amazon or Allegro.
Despite the progress made, Web 2.0 persists as a centralized internet landscape dominated by major tech players such as Google and Meta, who serve as overseers and disseminators of data. These corporate entities diligently collect information about our online interactions, utilizing them strategically in digital marketing campaigns, notably in the precise targeting of advertisements.
Web 3.0: The Decentralized Web
Now, we stand at the cusp of Web 3.0—the "read/write/own" upgrade. Rooted in decentralization, blockchain, and tokens, Web 3.0 champions user privacy, transparency, and ownership. It challenges the dominance of big data companies, ushering in a more democratic online world where users have greater control over their digital experiences.
Coined by Gavin Wood, the founder of Polkadot and a co-founder of Ethereum, the term "Web3" emerged in 2014, encompassing the concept of a "decentralized online ecosystem based on blockchain”. While the idea gained traction over the years, it experienced a surge in popularity in 2021, fueled by growing interest from cryptocurrency enthusiasts and significant investments from prominent technologists and companies.
In a revealing Wired magazine interview from 2021, Wood succinctly captured the essence of Web3 with the mantra: "Less trust, more truth." This simple yet profound statement reflects Wood's ambition to usher in a new era of the internet—one characterized by reduced dependence on centralized trust systems and a renewed emphasis on truthfulness. This departure from traditional models signifies a transformative shift toward a digital landscape that prioritizes transparency, decentralization, and user-centricity.
At the heart of this evolution towards a decentralized internet is the groundbreaking technology of blockchain, interconnected encrypted data chains, and cryptocurrencies. The very fabric of Web3 is woven with these innovations, empowering users with unprecedented control over their data, privacy, and digital interactions.
Certainly, the transition from Web2 to Web3 cannot occur without significant costs. Web2 has its advantages, mainly due to scalability and recognizability. We are accustomed to the technology we use daily, and transitioning to a different one—no matter how much it could improve our lives—can be challenging. Undoubtedly, more challenges will arise along the way, as Web3 must mature, but with the right timing and effort, they can certainly be mitigated.
As we navigate the evolving landscape of the internet, it becomes evident that contemporary technological innovations are laying the groundwork for the emergence of Web3. Key technologies serve as the driving force behind the transformative potential of Web3, ushering in a paradigm shift in our digital experiences.
Web3 Technologies Unveiled
As we explore the realm of Web 3.0, let's have a look at some of the key features and technologies that define what the new era of this digital landscape will likely be about.
Blockchain
Blockchain, an innovative technology, revolves around secure data encryption and is positioned to be the propelling force behind the decentralization of the current network. This technology empowers users to generate, store, and securely manage data independently, eliminating the need for intermediaries.
In contrast to the conventional centralized approach in developing web applications, blockchain technology ensures heightened security, transparency, and dependability. An additional pivotal aspect of blockchain technology lies in its capacity to automate processes through smart contracts—automated protocols executing specific functions, thereby enabling the automation of various processes and actions within web applications.
Furthermore, blockchain facilitates the development of personalized applications and their seamless integration. This allows users to transfer their data and preferences across diverse applications, spanning messaging platforms, browsers, data storage, or banking services.
Many applications and services now have decentralized counterparts that are continually evolving, thanks to forward-thinking companies embracing the spirit of the times.
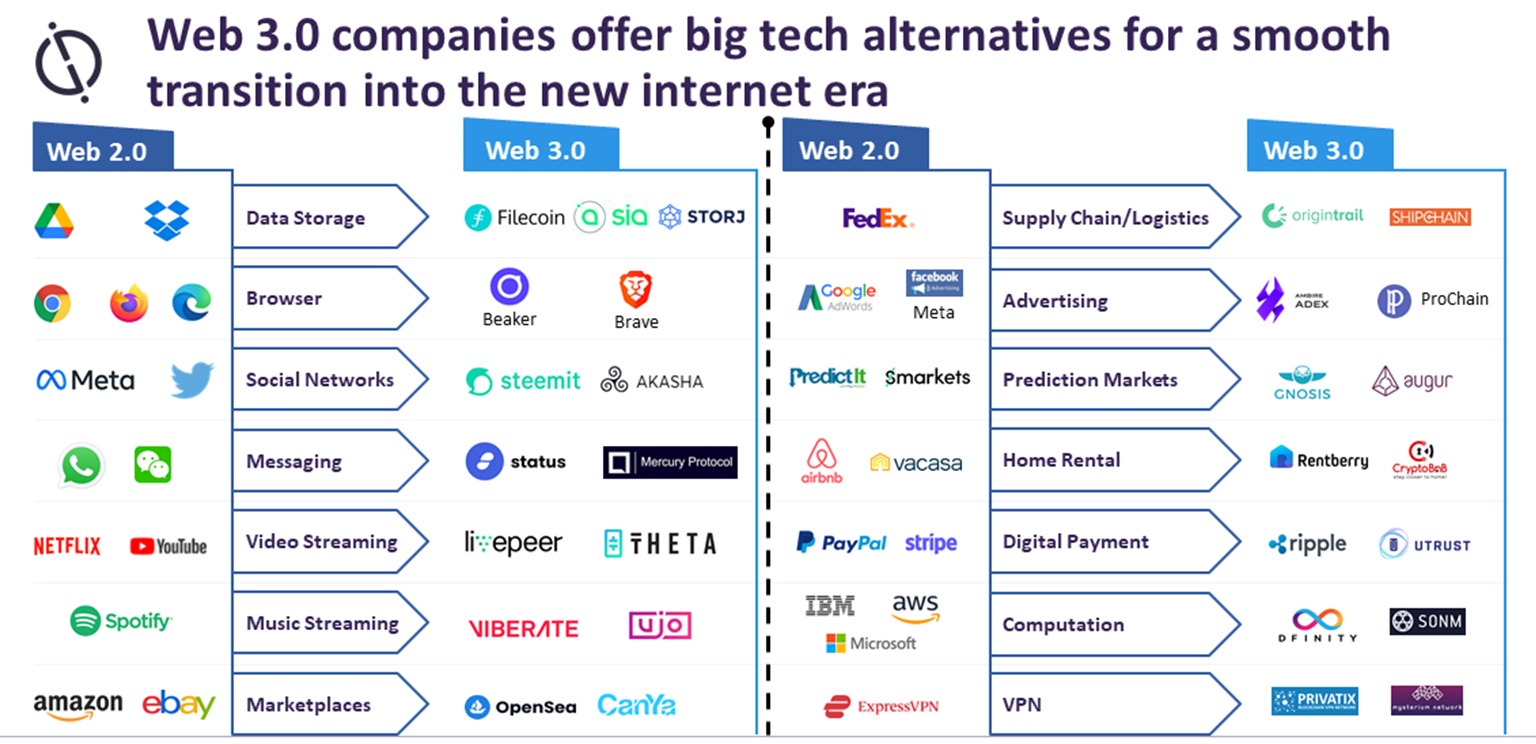 Many applications and services already have decentralized counterparts. Source: Oacer Web3 Services: The Future of Decentralized Applications
Many applications and services already have decentralized counterparts. Source: Oacer Web3 Services: The Future of Decentralized Applications
Decentralization
The use of blockchain technology allows for the distributed storage of data across various locations, removing the necessity for a central entity and freeing users from the oversight of large corporations. As a result, major technology companies such as Meta and Google will relinquish control over user behavioral data online, preventing them from utilizing this information for targeted marketing purposes.
DeFi: Decentralized Finance
DeFi aims to revolutionize finance by eliminating traditional intermediaries. Operating on blockchain, it promises reduced fees, accelerated transactions, and optimized capital allocation. Examples like Uniswap, Aave, and Chainlink showcase the potential for enhanced transparency and global accessibility, redefining the landscape of banking, lending, trading, and insurance.
Cryptocurrency
A secure, decentralized currency based on blockchain technology, such as ether or bitcoin, is poised to largely replace national currencies and payment intermediaries currently utilized in web2.
Artificial Intelligence and Smart Contracts
Artificial intelligence plays a crucial role in enhancing the capabilities of smart contracts within the Web3 framework. By integrating advanced decision-making capabilities, AI enables more intelligent and dynamic transactions on decentralized blockchain platforms. Smart contracts, acting as self-executing agreements with terms directly coded, automatically trigger predefined actions when specific conditions are met. This integration ensures increased trust, transparency, and transaction efficiency. With AI integration, smart contracts can tackle complex decision-making processes, leveraging data analysis, pattern recognition, and predictive capabilities.
NFTs: Non-Fungible Tokens
NFTs, unique digital assets on the blockchain, are rewriting the rules of ownership and authenticity. Beyond digital art, they offer tamper-proof identification, secure document authentication, and innovative crypto gaming experiences. Despite facing speculation challenges, NFTs have vast potential for impact, supported by blockchains like Ethereum, Solana, and Avalanche.
DAOs: Decentralized Autonomous Organizations
DAOs redefine collaboration in a decentralized world. Operating without hierarchy or bureaucracy, guided by smart contracts and member votes, they promise transparent financial health and inclusive decision-making. DAOs have the potential to revolutionize traditional corporate structures, offering a glimpse into a more democratic and equitable organizational future.
User Autonomy and Anonymity
The decentralized third-generation network will grant users greater independence, facilitating the creation of a censorship-free, democratized network where everyone can be a co-owner and collaborator. With enhanced data security in blockchain technology, Web3 will impede corporations' access to personal data and users' online behavior history.
Metaverse
The concept of the metaverse currently represents a concise term for virtual worlds. Within these realms, users experience heightened interaction and engagement with applications and services in a profoundly immersive way. This virtual environment is distinctly characterized by a focus on 3D graphics and real-world imagery, a departure from the prevalent 2D graphics and text found in today's web experience. In the metaverse, users don't merely click through links on a website; instead, they navigate through it virtually, contributing to a dynamic and visually rich online landscape.
What lies ahead
Web3 has the potential to address significant challenges of the contemporary internet and reduce the power of tech giants. Efforts toward developing the technologies that are likely to form the foundation of the next incarnation of the internet are already underway. Although we have only just begun to explore the full potential of these technologies, undoubtedly, we will benefit from the utilization of many upcoming features of Web3.


